From Aristotle to active investment management
From Aristotle to active investment management

Active investment management is consistent with the tenets of behavioral finance, as well as with sound financial planning that seeks to help investors reach their long-term objectives.
Over 2,500 years ago, in what may have been one of the earliest examples of behavioral finance theory, ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle is reported to have said the following regarding the achievement of success:
To my way of thinking, this captures much of the essence of modern behavioral finance theory: helping investors define clear goals, acquire knowledge around the many investing pitfalls that can derail the best investing intentions, and pursue a well-defined process (or “means”) to keep a long-term investment portfolio on track.
Far more recently, well-known figures in the history of the financial markets have provided their own takes on the psychology of markets and their participants.
Benjamin Graham, author of classics on fundamental and value equity investing, including the renowned book, “The Intelligent Investor” in 1949, wrote,
And, of course, Warren Buffett has offered many observations on market psychology over his long career. Although he has other far more popular quotes, this one resonates from a behavioral finance perspective:
“The most important quality for an investor is temperament, not intellect. You need a temperament that neither derives great pleasure from being with the crowd or against the crowd. … What you need is the temperament to control the urges that get other people into trouble in investing.”
BehavioralFinance.com provides this brief overview of the current state of behavioral finance theory:
“The groundbreaking work of psychologists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in the 1970s-1980s and the follow-on psychological research that has been conducted over the last three decades have revealed striking insights on the complex ways in which the human mind operates. This research identified pervasive, [deep-seated], subconscious biases and heuristics that occur in human decision-making, and revealed an entirely new perspective on why we behave as we do. While these revelations have their origins in psychology, they hold such important implications for the world of finance that Kahneman was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics. With the addition of recent Nobel Laureates Robert Shiller (2013) and Richard Thaler (2017), a total of six Nobel prizes have now been awarded for behavioral research. The body of work that has ensued thus represents an entirely new field of endeavor, referred to as behavioral finance and economics.
“The applications of behavioral science to finance are now broad and well researched. … Nonetheless, behavioral finance is still young and is only now beginning to make its way into mainstream academia, industry and society.”
In August 2020, Proactive Advisor Magazine published an article that showed how 2020 brought an environment that allowed some classic behavioral finance concepts to play out in a compressed time frame.
While the world has changed since then, much of that article remains relevant. Investors continue to navigate the fallout from the unprecedented COVID-19 era, including inflation, uncertainty over Federal Reserve interest-rate policy, ongoing supply-chain issues in several industries, and shifts in America’s workplace practices. Like in 2020, recession fears persist, the U.S. faces a potentially contentious election season, and market volatility has once again demonstrated this year how quickly it can soar and recover.
Says Creative Planning, “Over the past 10 years, we’ve witnessed market participants move from a state of panic to a state of calm with increasing speed. And over the last 9 trading days [8/5/2024 to 8/16/2024], we’ve experienced the biggest volatility crash in history, with the $VIX declining 62% (from 38.57 to 14.80 on a closing basis).”
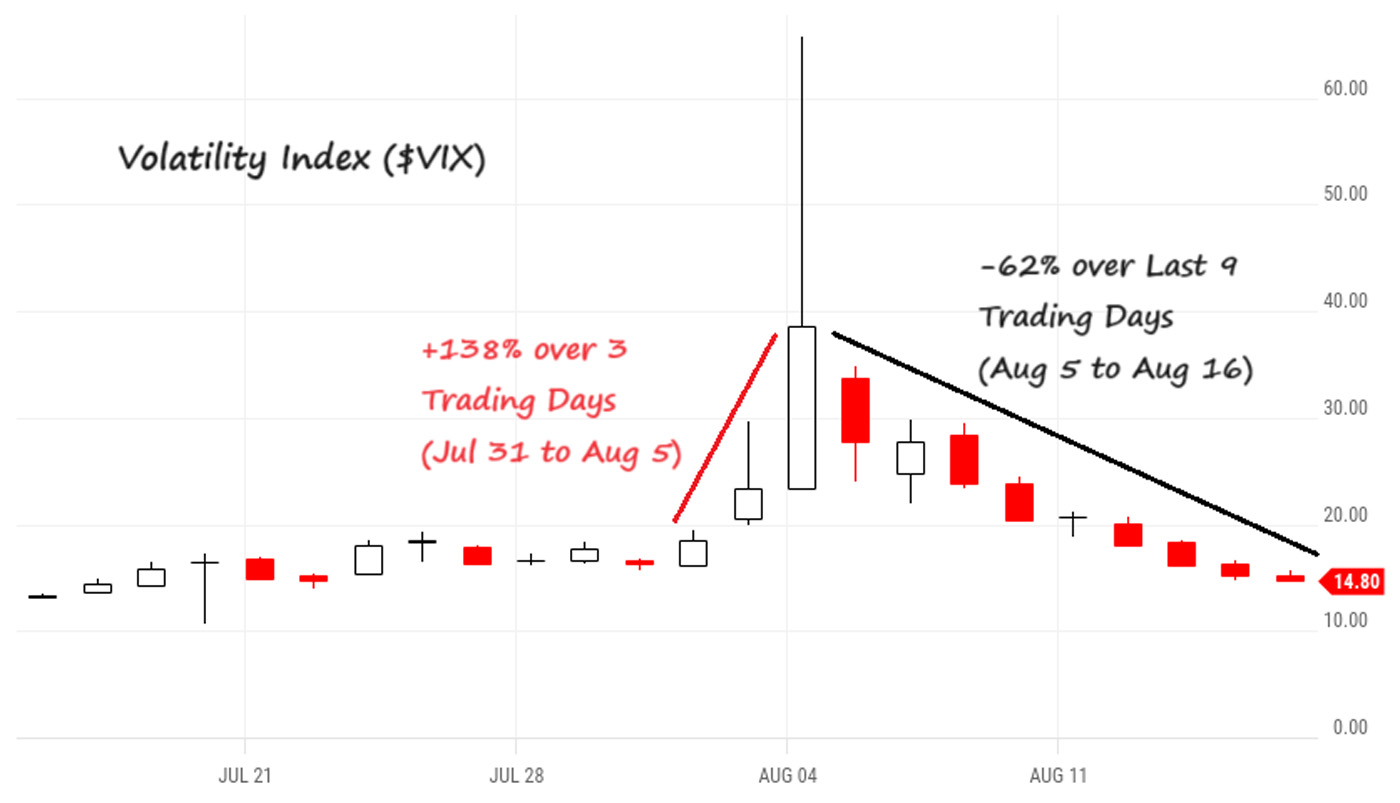
Sources: CBOE S&P 500 Volatility Index, Creative Planning
MarketWatch noted in late August that despite the rapid recovery from the volatility event and market tumble, the root causes may still present substantial risk for investors:
“A team of economists at the Bank for International Settlements decided to dig into what triggered the global meltdown that bulldozed financial markets on Aug. 5.
“They found that despite the chaos, markets held up remarkably well. But investors might not be so lucky next time—and there almost certainly will be a next time. As volatility recedes, traders have wasted no time rushing back into some of the same leveraged bets that contributed to the initial selloff. …
“‘[T]he factors behind the volatility spike and large market moves have not changed significantly. Risk-taking in financial markets remains elevated,’ the team said. …”
Against this background, financial advisors are increasingly recognizing the importance of behavioral finance theory in guiding their clients—especially in uncertain and volatile market environments. Many are pursuing continuing education in this discipline or even earning specialized certifications. Additionally, more coaching programs for financial advisors are incorporating behavioral finance as a key focus, with some coaches becoming specialists in the area.
Not surprisingly, a readership survey we conducted for Proactive Advisor Magazine showed that advisors are very interested in the topic of “applied behavioral finance.” (You can find numerous articles on the topic by respected academics, financial journalists, and investment managers in Proactive Advisor Magazine.)
Think Advisor reported in 2020 on how the COVID era impacted the adoption of behavioral finance practices by financial advisors:
“According to the second edition of an annual survey from Charles Schwab Investment Management (CSIM) and the Investments & Wealth Institute, conducted by Cerulli Associates, 81% of over 300 advisors said they’re using behavioral finance techniques in client communications and interactions, compared to 71% a year ago. …
“The big increase in advisors’ use of behavioral finance in client communications reflects their intensified efforts to help clients deal with the increased market uncertainty and life overall in this pandemic year, according to the Cerulli report. …
“Advisors using behavioral finance techniques were more engaged in tax-loss harvesting and increasing allocations to active managers than non-users. The latter focused more on reducing investment risk and increasing downside protection. …”
To this point about the value of active investment management from a behavioral finance perspective, a study from the nonprofit CFA Institute Research Foundation titled “Behavioral Finance—The Second Generation” notes,
The behavioral benefits of dynamic risk management and actively managed strategies
Richard Lehman, a professor of behavioral finance and founder of BehavioralFinance.com has noted in another article for our publication,
“Most investors do not behave in ways that are consistent with the theoretical benefits of long-term passive investing. They will likely be better served by an actively managed approach. …
“Risk tolerance and the desire for control are not constants among the investing populace, and behavioral studies also show that they vary with age, wealth, and life circumstances, not to mention the market environment. Many investors need tailored, flexible strategies that can dial the risk level up or down according to the variables mentioned above, getting more defensive or aggressive as conditions warrant. In most cases, active managers can supply these strategies better than the individuals themselves.”

Many active managers with a holistic portfolio management approach consider risk management at the core of their investment philosophy—seeking market opportunity but always keeping a close eye on mitigating risk.
One third-party investment management firm, a frequent contributor to our publication, says its suite of strategic solutions offers an effective way for investors to get the investment tools they need to traverse today’s markets. These turnkey solutions apply dynamic risk management at three different levels: within the funds used in their strategies, within the strategies themselves, and within the overall portfolio.
This approach can result in multiple benefits to investors:
- Access to sophisticated risk-management tools in an investment strategy that is customized to their risk tolerance.
- Confidence that their portfolio is working continuously to smooth out volatility.
- The long-term compounding advantage of helping avoid deep portfolio losses.
While being a market genius or investment-theory expert is appealing, it’s really not necessary. What is critical, as Aristotle, Graham, and Buffett suggest, is having a disciplined process that helps take emotions out of the equation. This is not only consistent with the tenets of behavioral finance but also with sound financial and investment planning that seeks to help each investor reach his or her long-term objectives.
The opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and the sources cited and do not necessarily represent the views of Proactive Advisor Magazine. This material is presented for educational purposes only.
This article was originally published in Proactive Advisor Magazine on October 20, 2020 (Volume 28, Issue 3). It has been revised to reflect updated information.
 David Wismer is editor of Proactive Advisor Magazine. Mr. Wismer has deep experience in the communications field and content/editorial development. He has worked across many financial-services categories, including asset management, banking, insurance, financial media, exchange-traded products, and wealth management.
David Wismer is editor of Proactive Advisor Magazine. Mr. Wismer has deep experience in the communications field and content/editorial development. He has worked across many financial-services categories, including asset management, banking, insurance, financial media, exchange-traded products, and wealth management.
