Does Warren Buffett believe in ‘market timing’?
Does Warren Buffett believe in ‘market timing’?

Professionals such as Buffett have worked out when they must sell an investment—whether things have changed for the better or for the worse. The average investor has no such plan.
The Berkshire Hathaway annual shareholder meeting last year drew over 30,000 people to Nebraska to hear the “Oracle of Omaha,” Warren Buffett. With the pandemic, this year the whole meeting was presented on the internet. Visit Omaha, the city’s tourism bureau, figures that will cost the citizens of that city about $21.3 million in lost compensation and revenues, according to The Wall Street Journal.
A company with a 20% compounded annual growth rate will definitely attract an audience. CEO Warren Buffett’s words of wisdom often entertain. More importantly, they are valued by investors worldwide. With the new virtual format, even investors who had not forked over the price of a share of Berkshire Hathaway stock, now close to $300,000 per share for the Class A version, could have listened in Saturday, May 2, to hear Mr. Buffett’s sage advice.
‘Buy and hold’ isn’t always enough—even for Warren Buffett
For average investors, Mr. Buffett’s advice continues to be that they should put their investable dollars in an S&P 500 Index fund and leave it alone. When coming from an investor worth about $70 billion, and ranked fourth in total worldwide wealth, these words have an impact.
I guess it would be easy to say in rebuttal that an investor with $70 billion can afford to lose 50% of their portfolio, as the S&P has done multiple times. After such a loss now, Mr. Buffett would still have $35 billion! The average investor with a portfolio designed to get them through retirement is not in such a fortunate position.
But there is much more wrong with this advice than just the size of the investor’s portfolio or their nearness to retirement. It also goes to the psychology of the strategy.
I have often stated that most investors cannot invest this way. Those who try seem to take one of two approaches. They either get frightened when the market falls substantially and sell (usually at the low point), or they stop opening their portfolio statements and just hold on to their investments. Two years later, these latter investors open their statements, see that they are likely still underwater, and end up delaying their retirement until they (hopefully) catch up.
In accumulating (and maintaining and growing) his great wealth, the path Mr. Buffett has taken is not the one that he recommended for others. He has indeed held many investments for a very long time. For example, he has spoken lovingly of his purchase of See’s Candies over 48 years ago.
Yet it is equally true that he has also bought and sold many companies over the years. Sometimes it was to upgrade his portfolio, other times it was to bring in a new sector or to sweep out an old one.
Still, at most of these meetings of late, we have not seen a lot of movement in the Berkshire portfolio. After all, we were in an 11-year bull market until very lately. It’s easy to buy and hold during such a period.
Let the good times roll! The test comes when the market falls precipitously.
At this year’s meeting, we learned a lot about how Mr. Buffett responds to just such an event.
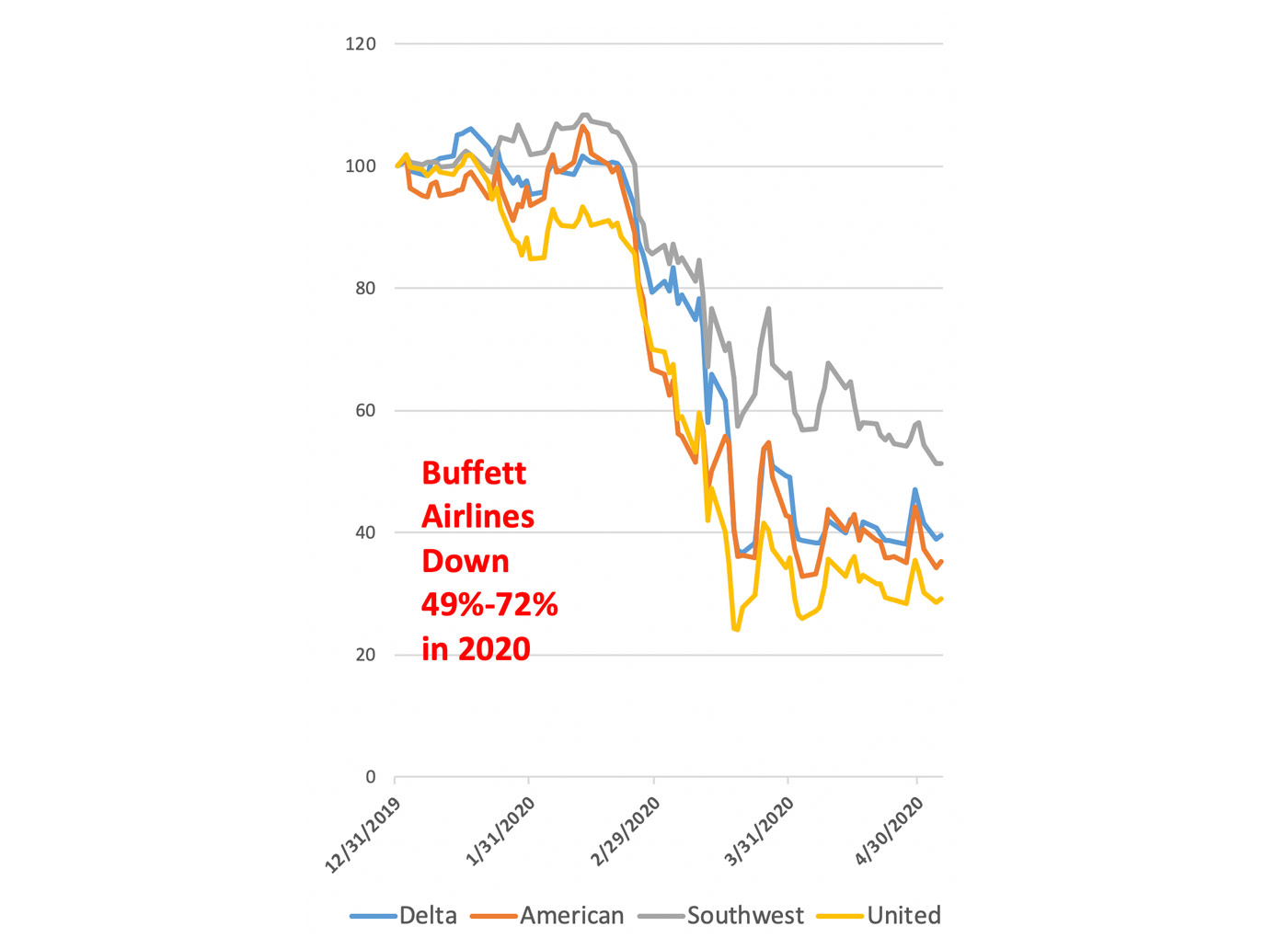
Let’s go back to Feb. 24 of this year. If you read the press about Mr. Buffett, you might remember his comment that if the market were to fall substantially Berkshire “certainly won’t be selling stocks.” Two and half weeks later, on March 13, he was more specific as he talked about the possible impact of COVID-19, proclaiming, “I won’t be selling airline stocks!” (He had even bought 1 million shares of Delta Airline stock just two weeks earlier to add to his already substantial investment in Delta and the Airline sector.)
At the shareholder meeting, we learned that Berkshire Hathaway sold all of its shares in the airlines in April. At that time, they disposed of their investments in Delta, American, United, and Southwest—all of it—over $8 billion in market value.
I know he says he isn’t a short-term trader, but he even sold the million shares of Delta that he bought just a month before.
Source: FPI Research
I don’t bring this up because I believe that Mr. Buffett misrepresented his intentions when he spoke to the press in February and March. I don’t believe that is the case at all.
For one thing, I have followed his career for decades and have too much respect for him to believe that. For another, I sincerely believe the truth of the reason that he gave for selling.
Warren Buffett said he dumped airlines because “the world has changed”:
“It’s obviously changed in the fact that the four companies are each going to borrow perhaps an average of at least $10 or $12 billion each,” Buffett noted. “You have to pay that back out of earnings over some period of time.” He then briefly praised the executives leading the airlines before adding this nugget of wisdom, “The airline business has the problem that if the business comes back 70% or 80%, the aircraft don’t disappear. You’ve got too many planes.”
I can’t fault the reasoning. And I think the same reasoning applies to office and retail real estate, malls and retail stores, hotels, and the whole travel industry. How about Disney? As of the writing of this article, theaters are closed and can’t show its films, its theme parks are closed, and its cruise ships are idle at the docks. Just about everything, in everyone’s lives, has changed due to the pandemic this year.
That’s this time around. But how about when the tech stocks got so overvalued that it sparked a 70% correction in 2000–2002? Or in 2007–2008 when many Americans lost their homes, banks closed, and people who were about to retire could no longer consider it?
Yes, the world has changed now, but history demonstrates that it has a habit of doing that to a greater or lesser degree with some regularity. Yet buy-and-hold investing doesn’t allow for that possibility.
Berkshire Hathaway at the end of the first quarter 2020 had about $137 billion in cash. This didn’t come from the airline sales. Those appear to have been made in the second quarter. No, it came from many years of not just buying and holding. It resulted from a policy of not just plowing profits back into existing stock market investments. It was deliberately allowed to accumulate.
When he was asked why his company had not invested this great horde of cash, he said that, even after the more than 30% fall in the S&P since its Feb. 19 high, “we don’t see anything that attractive.”
And it also came out at the meeting that, although the company had bought back more than $1.6 billion of its own stock early in the first quarter, it had made no more purchases after March 10. One of the more interesting parts of the meeting was Mr. Buffett explaining why he had been doing billions of dollars of buybacks of his shares for many years at higher prices, and had done so again early in the quarter, but could not find the value in doing so now … at lower prices.
Did he think that the value would go lower? He has made a great deal of money buying when prices were low and selling when they were higher.
Now what is that called? It starts with a “T” and ends with a “G” and whether you decipher that as “trading” or “timing,” it sure isn’t buy-and-hold investing.
Professional investors such as Warren Buffett have worked out when they must sell an investment—both when things have changed for the better and when they have changed for the worse. The average investor has no such plan. Nor does Mr. Buffett offer them one. Yet the world is always “changing.”
Rather than investing without a plan of when to buy and sell, at Flexible Plan Investments we have spent almost 40 years developing quantified, disciplined methodologies for doing so for investors with as little as $5,000. That’s not nearly enough to buy even one share of Class A Berkshire Hathaway, but it suits our purpose of delivering professional investor approaches to the average investor.
The opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily represent the views of Proactive Advisor Magazine. These opinions are presented for educational purposes only.
This is an edited version of an article Mr. Wagner first authored on May 5, 2020.
 Jerry C. Wagner, founder and president of Flexible Plan Investments, Ltd. (FPI), is a leader in the active investment management industry. Since 1981, FPI has focused on preserving and growing capital through a robust active investment approach combined with risk management. FPI is a turnkey asset management program (TAMP), which means advisors can access and combine many risk-managed strategies within a single account. FPI's fee-based separately managed accounts can provide diversified portfolios of actively managed strategies within equity, debt, and alternative asset classes on an array of different platforms. flexibleplan.com
Jerry C. Wagner, founder and president of Flexible Plan Investments, Ltd. (FPI), is a leader in the active investment management industry. Since 1981, FPI has focused on preserving and growing capital through a robust active investment approach combined with risk management. FPI is a turnkey asset management program (TAMP), which means advisors can access and combine many risk-managed strategies within a single account. FPI's fee-based separately managed accounts can provide diversified portfolios of actively managed strategies within equity, debt, and alternative asset classes on an array of different platforms. flexibleplan.com
